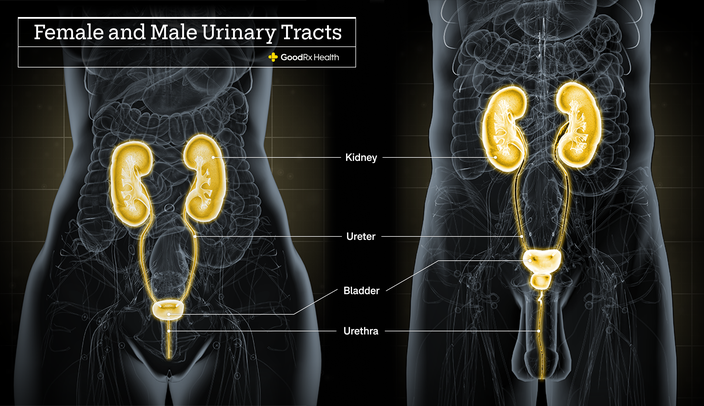
The urinary tract is a crucial part of the body’s system for eliminating waste and maintaining fluid balance. It consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, each playing a vital role in filtering blood, removing waste, and regulating electrolyte levels. The primary function of the urinary tract is to remove waste products and toxins from the bloodstream, which are then excreted as urine.
This helps prevent the buildup of harmful substances in the body.
Let’s look at each organ and its function
Kidneys:
- Two bean-shaped organs located on either side of the spine.
- They filter blood to remove waste products and excess substances, forming urine.
- They also regulate blood pressure, produce hormones, and maintain overall fluid balance.
Ureters:
- Tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Each kidney has one ureter.
Bladder:
- A hollow, muscular organ that stores urine until it is ready to be expelled from the body.
- The bladder can expand to hold varying amounts of urine.
Urethra:
- A tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body.
- In men, the urethra also carries semen and is longer than in women.
The kidneys regulate the body’s fluid balance by adjusting the amount of water excreted in urine.
They also balance electrolytes (e.g., sodium, potassium, calcium) essential for nerve function, muscle contraction, and other physiological processes.
The kidneys help regulate blood pressure by controlling the volume of blood (through fluid regulation) and releasing the enzyme renin, which influences blood pressure.
The kidneys produce erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow in response to low oxygen levels in the blood.
The kidneys help maintain the acid-base balance (pH) of the blood, ensuring it stays within a narrow, healthy range.
Infections:
UTIs can cause discomfort and, if untreated, may lead to more severe kidney infections (pyelonephritis).
- Kidney Stones:
Hard deposits can form in the kidneys, causing pain and potentially obstructing urine flow.
- Chronic Kidney Disease:
Long-term damage to the kidneys can impair their ability to function, leading to waste buildup and other health issues.
- Bladder Disorders:
Conditions like interstitial cystitis or bladder cancer can impact urinary function and quality of life.
- Prostate Issues (in Men):
An enlarged prostate can obstruct the urethra, leading to urinary retention and increased infection risk.
Maintaining a Healthy Urinary Tract
- Hydration:
Drink plenty of water to help the kidneys filter waste and prevent the formation of kidney stones.
- Diet:
Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to support overall health.
- Hygiene:
Practice good personal hygiene to reduce the risk of infections.
- Regular Check-ups:
Routine medical exams can help detect and manage potential urinary tract issues early.
- Avoid Holding Urine:
Regularly emptying the bladder can prevent infections and other complications.